|
posted by transport blogs
@ 10:53 PM
permanent link |
|

The following general guidelines address food safety measures that should be taken by shippers from the point of food production through delivery. The guidelines do not cover breeding, feedlot, or any other pre-slaughter live-animal operations or pre-shipment operations at egg-laying farms. TRANSPORTATION SAFETY PLAN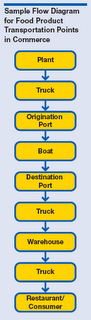 - Identify vulnerable points and develop a comprehensive transportation sanitation and safety plan.
- Processors and distributors shipping products should assess and implement measures that will ensure the sanitation and safety of products from initial shipment through delivery to other destinations. A flow diagram from the point-of-origin to final destination, including all shipping modes/routes, can be a helpful assessment tool. (See Attachment for sample flow diagram.)
- Identify all points of vulnerability where there is potential for adulteration or contamination to occur:
- Identify potential hazards.
- If control points are identified, then determine the method, frequency, and limit that must be met.
- Identify if control is possible at the point(s) of hazard and what is the most effective point to exert control.
- This will determine where and how often monitoring and verification of the limits set should occur and what, if any, corrective and preventive actions should be taken.
- Define what controls should be put in place to prevent product adulteration or contamination during the transportation and storage process.
- As an additional check on product condition during and after transportation and storage, processors may want to include special arrangements with receivers to sample and conduct microbiological or other tests on products. The results could be compared with pre-shipment results to determine whether adjustments are needed in transport methods or procedures.
- Verify that contracted transporters (e.g. air, ground, maritime, rail) and storage/warehouse facilities have a food safety program in effect. Consider including specific security measures in contracts and verify that measures are being met.
- Include procedures for the immediate recall of adulterated products from trade and consumer channels (this applies to processors, transporters, and wholesale and retail distributors).
- Have a system in place to track your products, including salvage, reworked, and returned products.
Source: http://www.fsis.usda.gov/ Labels: Food Transportation Safety Plan










posted by transport blogs
@ 12:22 AM
permanent link |
|

posted by transport blogs
@ 10:44 PM
permanent link |
|

posted by transport blogs
@ 9:49 PM
permanent link |
|

 The U.S. marine transportation system encompasses a national and global network of navigable ocean, lake, river, and inland waterway routes; the vessels that carry waterborne commerce; a complex of ports and terminals serving as inter modal points of transfer between the water system and the land-based transportation modes; ship operators; an extensive supplier base; and shipboard, shipyard, and long shore labor forces. The system includes over 3,500 bulk oil transfer facilities, 10,000 marinas, 18,000 bridges, a network of locks and dams, and 97,000 aids to navigation. Diverse groups of waterway users commercial vessels making 70,000 port calls annually, 110,000 fishing vessels, and 20 million recreational vessels vie for access to our waterways often with conflicting interests and purposes. Additionally, the general public is concerned about the waterways environmental health and esthetics.
Source: http://www.yoto98.noaa.gov/ Labels: Present U.S. Marine Transportation System












posted by transport blogs
@ 4:10 AM
permanent link |
|

 Sri Lanka is strategically located in the Indian Ocean at the centre of east-west maritime routes. In the late-90s, the government took a decision to develop Sri Lanka as a regional shipping and logistics hub similar to Dubai, Singapore and Hong Kong. The Port of Colombo has undergone cycles of expansion and modernisation to meet the needs of the shipping industry both domestically and globally. The development is continuing. The Port of Colombo has 23 major shipping lines and seven feeder services in operation, and is considered one of the most efficient and streamlined ports in the region. The port has two modern container terminals, equipped with state of the art technology and IT systems. It has an annual cargo handling capacity of 2.5 million 20-foot equivalent units (TEU). Transhipment cargo accounts for over 70 per cent of the total. Of the transhipment cargo, 85 per cent is Indian container business. Throughput at the port has grown at an annual compound rate of 20 per cent per annum over the past 10 years. The development of the port facilities has included: - Ancillary support services
- Cargo logistics operations
- State-of-the-art warehousing facilities
- Multi-country cargo consolidation
- Container freight stations
- Computerised container depots
The port system has growing capacity and efficiency; port services performance increased by 16.9 per cent in 2005 compared to an increase of 12.8 per cent in 2004. Source: http://www.austrade.gov.au/ Labels: Port Development Activities To Sri Lanka












posted by transport blogs
@ 10:24 PM
permanent link |
|

posted by transport blogs
@ 10:25 PM
permanent link |
|

 Inland Water Transport (IWT) is an economic, fuel-efficient and environment friendly mode of transport. India has an extensive network of rivers, lakes and canals which, if developed for shipping and navigation, can provide an efficient network of inland transportation. An optimal mix of road, rail and inland water transport will provide an efficient transport infrastructure with mobility, flexibility and cost effectiveness. While the thrust so far has been in developing road and rail sectors, Government recognizes the need to actively promote the IWT sector for it to take a reasonable share in the inter-modal mix of inland transport.
The Inland Waterways Authority of India Act, 1985 empowers the Government to declare waterways with potential for development of shipping and navigation as National Waterways and develop such waterways for efficient shipping and navigation. So far, waterways namely, the Ganga, the Brahmaputra and the West Coast Canal have been declared as National Waterways and are being developed for shipping and navigation by the Central Government.
The revival plan of Inland Water Transport would include increasing the coverage of National Waterways and provision of necessary infrastructure for shipping and navigation and in augmenting the IWT fleet. While there would be a need for budgetary support for the development of the IWT sector, equally important would be a large-scale private sector participation both for creation of infrastructure and for fleet operations.
The IWT strategy aims at generating a more pro-active role by various agencies for the development of this sector. It has now been decided to enlarge the scope of the role of the Government as a provider, facilitator and regulator and, at the same time, offer various concessions to the private sector for their effective participation by way of investment for creation of enhanced IWT infrastructure and fleet operations.
Source: http://business.gov.in/ Labels: Inland Water Transportation












posted by transport blogs
@ 10:05 PM
permanent link |
|

 Range of roles in water transportWater transport jobs range from shore-based roles, such as check-in agent and radio operator, to jobs on the water, such as harbour pilot and ship's master. Volume of exports and imports affects water transport opportunitiesThe volume of New Zealand's exports and imports influences opportunities in the water transport industry. Because of New Zealand's export-driven economy and geographic isolation from major markets, almost all of our imports and exports are moved by ships (99.5% and 99.4% by weight, respectively). Exports likely to growExports are expected to continue growing due to: - New Zealand recently signing a free trade agreement with China, which has reduced the tariffs New Zealand businesses pay to export goods to China
- The 2008 recession and the New Zealand dollar losing value compared with some other currencies, resulting in overseas customers buying more New Zealand goods.
Shipping favoured by governmentThe Government has singled out shipping as its favoured method of moving freight because it is more energy and cost-efficient than road, air or rail transport. In the Ministry of Transport's Sea Change policy document, the Government states that it will double the amount of domestic freight moved by ship, from 15% in 2007 to 30% in 2040. This will increase demand for people in roles such as ship's masters, harbour pilots and stevedores. Exemption from Kyoto Protocol likely to result in increased shippingEmissions from ships are not regulated under the Kyoto Protocol. This means that, unlike road transport businesses, companies that shift goods by ship will not have to pay for the amount of CO2 they emit. This is likely to mean that even more goods will be transported by ship than before, creating demand for more water transport workers. Possible changes to water transport training and qualificationsThe Sea Change document notes that there are some inconsistencies with training in the water transport industry, and aims to put them right. Maritime New Zealand is reviewing its qualifications currently, and the Tertiary Education Commission is reviewing its policy of not making training grants available for the at-sea component of training programmes. Source: http://www.careers.govt.nz/ Labels: About Water Transport industry












posted by transport blogs
@ 10:22 PM
permanent link |
|

posted by transport blogs
@ 10:28 PM
permanent link |
|

posted by transport blogs
@ 10:01 PM
permanent link |
|

This Strategy Aims to Protect Coastal Waters through Partnerships with Shipping Industries The ability of Australia and New Zealand to protect coastal and offshore waters from shipping pollution has been strengthened with the June 1996 release of a joint government strategy. Entitled Working Together to Reduce Impacts from Shipping Operations: ANZECC Strategy to Protect the Marine Environment, the strategy pulls together a number of initiatives developed by ANZECC's Standing Committee on Environmental Protection. These initiatives promote: - Improved port waste reception facilities;
- Better management of marine debris and ballast and hull transfers;
- Communicating better with shipping about environmentally sensitive operations;
- More benign anti-foulants; and
- Education and outreach programs.
Three national surveys completed during 1996, provide important baselines for evaluating future improved performance and management on waste reception facilities at ports, boat harbours and marinas and marine debris research and management strategies. What is the strategy's objective? This national Strategy aims to enhance the protection of the marine environment through promoting best practice to improve waste management and to reduce pollution from shipping, and to communicate effectively with shipping about environmental values. Its Action Plan covers 12 issues:1. communicating about areas sensitive to shipping and boating operations; 2. managing contaminated ballast and hull transfers; 3. improving port waste reception facilities; 4. improving anti-fouling practices; 5. managing marine debris; 6. involving the community; 7. promoting education and outreach programs; 8. promoting targeted and resourced research; 9. developing industry action; 10. contributing to IMO and other international activities; 11. promoting improved shipping standards; and 12. promoting use of environmental impact assessment. Source: http://www.environment.gov.au/












posted by transport blogs
@ 9:30 PM
permanent link |
|

 The volume of goods transported of waterway of our country and rotation volume of goods transport will account for 12% and 62% in the comprehensive transportation system respectively in 2006, bear more than 90% of the foreign trade traffic volume, unload more than 95% imported crude oil and 99% of the imported iron ore in our country at the port. Such one group data, enough to reflect water way carrier in leading status of the large freight transportation, energy, raw materials,etc. of our country, it is enough to prove the water way carrier is developed in our country's economics and society and foreign trade, ensure national economical operation important guarantee function in being safe.
What is promoting the swift and violent development of the water transport industry of our country? National conditions Hu Angang, director of research center, make the transition that that development strategy analyze at the seminar from traditional industry to modern service trade in traffic that will it be the end May hold just as Tsing-Hua University Kind, the demand is spured, technological progress and system innovation are three major reasons that traffic trade develop at full speed. Behind what the water transport industry of our country developed rapidly, have enormous demand brought in high-speed development of economics and society of our country to pull, have a large number of water transport scientific and technical innovation effective support of achievement, have port management system, water supervise management system, rescue system reform of dragging for safely even more, water transport strategical planning and laws and regulations completion of system, and water transport foundation of market system wait, show to push with strength trade management of effect a series of day.
http://www.fjjt.gov.cn/












posted by transport blogs
@ 8:54 PM
permanent link |
|

posted by transport blogs
@ 9:34 PM
permanent link |
|

 The following information has been developed to help employers and employees develop an effective fire protection program. This involves protecting shipyard employment workers from fire hazards while conducting ship repair, shipbuilding, shipbreaking, and related work activities as well as firefighting activities. Many of the basic tasks involved in shipyard employment, such as welding, grinding, and cutting metal with torches, provide an ignition source for fires. There are also many combustible materials on vessels and in shipyards, including flammable fuels, cargo, wood structures, building materials, and litter. When torches are used in confined or enclosed spaces, accidents resulting in oxygen-enriched atmospheres can cause normally fire-resistant materials to readily burn. When fires do occur, employees are often working in confined or enclosed spaces making escape difficult or impossible. Fires in such confined or enclosed spaces can also result in atmospheres of combustible gases, toxic fumes, or oxygen-deficient air or super-heated air. When the worksite has multiple employers, the host employer (typically the shipyard or the owner of the vessel) and the contract employer must assure: [1915.501(d)] - That their fire safety plans are compatible (include hazards, controls, fire safety and health rules, and emergency procedures), and
- That all employees are familiar with the plan.
- That the plan is accessible to all employees.
Source: http://www.osha.gov/












posted by transport blogs
@ 9:18 PM
permanent link |
|

posted by transport blogs
@ 9:40 PM
permanent link |
|

posted by transport blogs
@ 10:09 PM
permanent link |
|

|

![]()

![]()
























